We often receive calls from clients stating that they have installed new LED bulbs into their commercial, institutional, or theatrical (non-residential) lighting control systems and they can no longer dim the LED bulbs properly. Are you having issues dimming your LED lamps? What are some of the items you should consider when installing LED lamps into your dimming system? How can you test for LED lamp compatibility with your dimming system? Why do forward phase and reverse phase dimming matter? Here are some of our conversations around why your LED bulbs might not be integrating properly into your lighting system.
WHY SWITCH TO LED LAMPS? THERE IS TREMENDOUS ENERGY SAVINGS AND COST SAVINGS.
We have successfully replaced many incandescent systems with new LED lamps and have had tremendous success. Why switch to LED lamps? The biggest reason is the amount of energy you save by using an LED lamp which can be about a 20 times (or larger) savings over an incandescent lamp or 6 times savings for an LED lamp versus a fluorescent lamp.
What is the advantage of LED lamps over fluorescent lamps?
- LED lamps can save 20 times the energy of incandescent lamps; 6 times the energy of fluorescent lamps
- LED lamps produce less heat so your HVAC costs are lower
- LED lamps are not considered hazardous materials (there is mercury in fluorescent lamps)
- LED lamps do not break nearly as easily as a fluorescent tube
- LED lamps longer life reduces maintenance staff time to change out the lamps (think here of less time on ladders, lifts, and scaffolding replacing lamps)
WHY ARE MY NEW LED LIGHTS FLICKERING ON THE DIMMING SYSTEM? THE MOST COMMON CAUSE IS LACK OF RESISTANCE IN THE LAMP.
As many of you may have found out, not all LED lamps and/or LED lighting fixtures are created equal. A common problem that we run into within our industry is when a customer wants to replace their existing incandescent lamps with new highly efficient LED lamps and/or LED lighting fixtures. When they change out all of their LED lamps and/or LED lighting fixtures and then turn them on, they often find them flickering.
There are many reasons why an LED lamp can flicker, but the most common cause is a lack of resistance in the lamp to allow the dimmer curve to work correctly. This is not a new issue; it’s been around for a long time, but is becoming more “noticeable” with the major increase in LED usage. We first saw this issue when dimmable fluorescent lamps and/or dimmable lighting fixtures became popular several years ago. The same issue occurred at that time, because the fluorescent lamp does not have enough resistive load between the load and neutral wires (complete circuit).
Over the years, we have done many things to try to stop that flickering issue with the fluorescent lamps and now with the LED lamps. The biggest key is often to add resistance, but this does not always fix the problem. Many dimming manufacturers and LED manufacturers are now working together to prevent this issue. However, since there are so many new LED lamp manufacturers, it is hard to achieve much consistency within the industry.
We would recommend the Renesola and Canto Lines of LED lamps, because they are both forward phase dimmable LEDs.
HOW CAN YOU TRY TO AVOID LED LAMP DIMMING ISSUES? TEST FIRST - ON ONE CIRCUIT.
The quickest advice I can give you at this time is try out the LED lamps and/or LED fixtures on one circuit, before you order a whole lot of LED lamps. I recommend taking a circuit with between 1-5 lamps on it to replace with the LED lamps and/or LED fixtures. If the LED lamps will work on this type of circuit, then odds are high that it will work on the rest of your circuits.
What are the LED manufacturers doing to correct this issue? As mentioned above, they are getting together with the dimming manufacturers and are working on solutions. A simple solution is for the LED lamp manufacturers to add a resistant circuit to each lamp, which helps with the dimming process. In addition, the dimming manufacturers are coming out with many new types of dimmers, which help to address the need for very little resistance on the dimmer by either adding resistance to the load or using different types of dimming such as forward phase or amplitude dimming. However, if you already have dimmers, it hardly seems like a fair trade to replace your dimmers to install LED lamps and/or lighting fixtures.
WHY DO “REVERSE PHASE” DIMMERS WORK BETTER THAN TRADITIONAL “FORWARD PHASE” DIMMERS FOR LED LIGHTING?
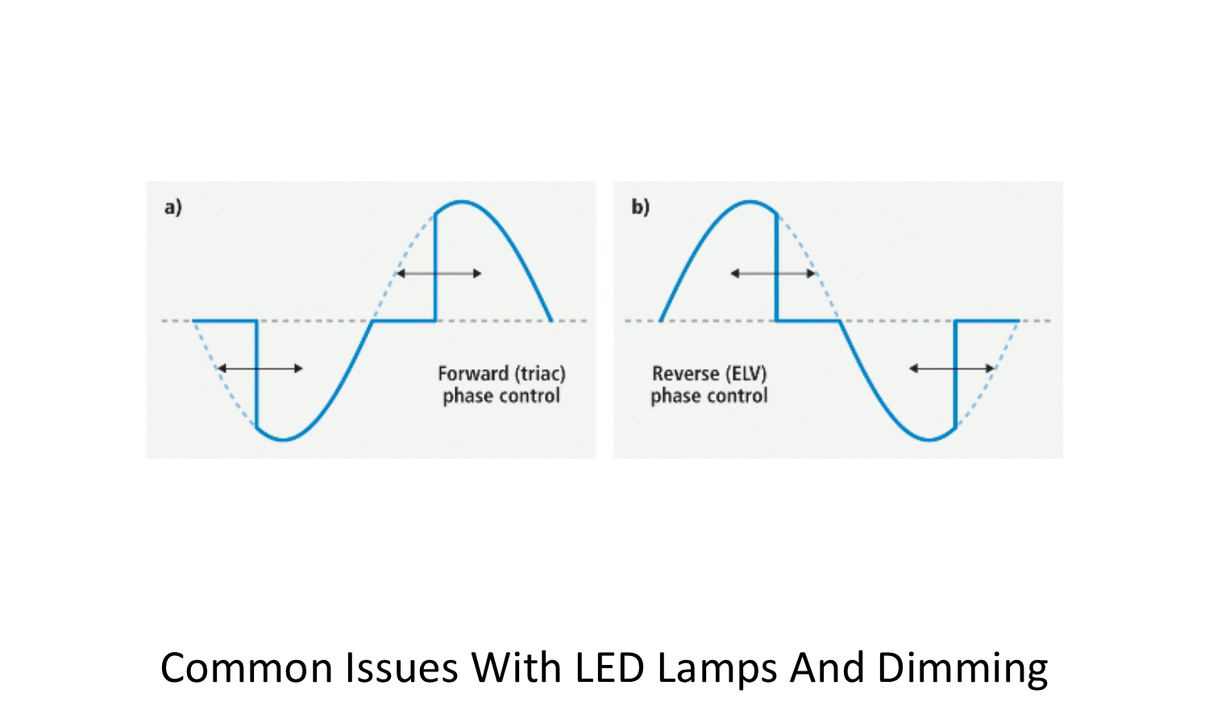
What is the difference between traditional "Forward Phase" Dimming and newer "Reverse Phase" Dimming technology? The distinction is important because of LED lamps and drivers (drivers are the electronics that run the LED lamps). The lack of resistance in LED Drivers can cause problems in the dimming of LED lamps. How can a Reverse Phase Dimmer help to correct the issue of a lack of resistance in the LED lamps driver and electronics? The simple answer is the cycle of power and how it is applied with a Reverse Phase or ELV Dimmer. The diagram below shows both a Forward Phase (Triac based; Diagram A-on left) and a Reverse Phase (ELV based; Diagram B-on right) Dimmer Curve.
 Now that you have seen the images of the Forward Phase and Reverse Phase Dimmer Curve, what exactly are we looking at in the image? If you think left to right (just like in reading), when you look at the images, then the power is coming from the left edge and then is flowing out of the right edge. In Image A (Forward Phase Dimming), you see that the power comes in from the left, but is suppressed or prevented from operating until it has gone through approximately 1/3 of the cycle (this is shown with the dots on the curve). Then the power comes in quickly from the crossover line (center horizontal line) and goes to the correct level. Whereas on Image B (Reverse Phase Dimming), the power comes in normal through approximately 2/3 of the cycle’s wave and then is cut out or suppressed for the last 1/3 of the cycle’s wave.
Now that you have seen the images of the Forward Phase and Reverse Phase Dimmer Curve, what exactly are we looking at in the image? If you think left to right (just like in reading), when you look at the images, then the power is coming from the left edge and then is flowing out of the right edge. In Image A (Forward Phase Dimming), you see that the power comes in from the left, but is suppressed or prevented from operating until it has gone through approximately 1/3 of the cycle (this is shown with the dots on the curve). Then the power comes in quickly from the crossover line (center horizontal line) and goes to the correct level. Whereas on Image B (Reverse Phase Dimming), the power comes in normal through approximately 2/3 of the cycle’s wave and then is cut out or suppressed for the last 1/3 of the cycle’s wave.
Both Forward Phase Dimming and Reverse Phase Dimming provide the exact same amount of energy to the light fixture, which they are powering. The BIG difference is that with Reverse Phase Dimming, the electronics in a LED Driver and/or Fluorescent Ballast are powered FIRST and then the dimming occurs second. Physically, we can not see the difference in the two types of Dimming, but the LED Driver and/or the Fluorescent Ballast sure notices the difference and will respond VERY differently to the two types of Dimming Styles.
Almost all dimmers made in the world prior to the year 2010 were Forward Phase (Triac Based) Dimmers. That is why a lot of time, the LED Drivers and/or Fluorescent Ballast do not work well when connected to existing dimmers. Since there are so many Forward Phase Dimmers around the world, the leading LED manufacturers are working with the Dimmer Manufacturers to try to make their LED Lamps/Drivers work with Forward Phase Dimmers. However, since LED Lamps/Drivers is a growth industry and it seems like everyone is getting into the industry, there is a lot of room for error in the design of the LED lamps and/or drivers to work with Forward Phase Dimmers.
If you need to convert your forward phase dimmer to a reverse phase dimmer, then the Leviton PE400 Power Extender will convert a forward phase dimmer to a reverse phase dimmer output.
When you are choosing an LED Lamp, LED Driver, Fluorescent Lamp, and/or Fluorescent Ballast make sure that is Forward Phase Dimming Capable. This is really important if you have existing dimmers.
One note is that the Fluorescent lamp and ballast manufacturers have already worked out a lot of these issues and the vast majority of Fluorescent lamps and ballast that say “dimming capable” are Forward Phase Dimming Capable.
If you are doing new projects and can select both the LED Lamps and Drivers for your project, then you should take some time and plan accordingly. Yes, you can purchase Reverse Phase Dimmers from several lighting manufacturers, which will work very well with dimming capable LED Lamps and Drivers. Again, you must make sure that the LED Lamps and/or Drivers are dimmable, even with a Reverse Phase Dimmer. Several LED Lamps and Drivers are NOT dimmable and will not work, whether you use a Forward or Reverse Phase Dimmer.
Hopefully, this very basic discussion of issues around LED lamps and dimming will provide you with some more context when planning your next lighting project. Please keep in mind that Knight Sound & Lighting can help you with your project planning, bill of materials, or technical issues when you are working on dimming and control options for your facility. Please call us at 1-866-457-5937 if you would like to speak to a lighting technician about your system.
Source: Interview with Mark A. Knight, CEO of Knight Sound & Lighting
Additional Resources:
- Leviton LED Control Solutions: http://www.leviton.com/en/solutions/leviton/energy...
- LED theatrical lighting fixtures: https://www.chauvetprofessional.com/stephen-elliso...
- Residential LED savings calculator: http://www.leviton.com/en/products/lighting-contro...
- LED lighting Dept. of Energy: https://energy.gov/energysaver/led-lighting
- Understand compatibility of LED lamps and dimming: http://www.ledsmagazine.com/articles/iif/print/vol...
- Ohio First Energy Lighting Incentive Program for Commercial & Industrial Energy Efficiency Programs: http://www.energysaveoh-business.com/lighting-prog...
- Learn About LED Bulbs: https://www.energystar.gov/products/lighting_fans/...
- ETC LED Fixture Test Results: https://www.etcconnect.com/About/News/The-test-res...
- Lutron LED Center of Excellence: http://www.lutron.com/en-US/Education-Training/Pag...